In an increasingly interconnected world driven by technological advancements, a looming crisis has captured the attention of industries, governments, and individuals alike: the semiconductor chip shortage.
Have You Ever Wondered Why the Semiconductor Industry is a Billion-Dollar Industry?
The semiconductor industry is a billion-dollar industry because a world without semiconductors would be a world without smartphones, LED TVs, automated machines, advanced automobiles, high-tech medical equipment, and robots. Today, semiconductors are at the heart of the digital world. Smart technology employs semiconductor chips. America is at the forefront of semiconductor manufacturing, delivering cutting-edge semiconductor equipment and semiconductor chips, earning half of the semiconductor industry’s global sales. On February 23, 2023 Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) made a huge announcement, stating the all-time high annual global semiconductor industry sales in 2022, which totaled $573.5 billion. This booming semiconductor industry is spurred by the demands of the consumers to break new ground with advancing technology nodes.
What was the Major Issue with the Electronics of the Past?
The major issue with electronics of the past, before the inception of semiconductor chips, was their large size. Electronic components used vacuum tubes and were not power efficient. With the invention of Integrated Circuits, or ICs, and the revolutionization of semiconductor manufacturing processes, transistors have become smaller and smarter. Miniaturization of transistors enabled millions of transistors to be accommodated in a device, increasing the computational power of leading-edge devices. Staying true to Moore’s law, transistors have come a long way from a 3 micron (μm) technology node to a 5 nanometer (nm) technology node.
What was Gordon Moore’s Prediction?
Reflecting on the words of William Blake, who said, “What is now proved was once only imagined,” we come to realize that the extraordinary possibilities we witness today through semiconductors were just an imagination of the past. It was a prediction or an imaginative thought of Gordon Moore who boldly stated that “the density of transistors used on an integrated circuit would increase double-fold and the cost of electronics would gradually decrease every year.” Moore did not live to see his prediction being proved but his prediction has impacted the trajectory of technological progress.
What Helped in the Evolution of Technology Nodes?
The evolution of technology nodes was accelerated by the advancement in Front End Of Line (FEOL), Middle Of Line (MOL), and Back End Of Line (BEOL) of an IC. Advancements such as the invention of Fin Field Effect Transistors (FinFETs), the transition to high-K gate dielectric and low-K interlayer dielectrics, the introduction of strain technology, and the adoption of copper interconnects enabled the evolution of technology nodes. Recently, manufacturers have recognized the limitations of FinFETs when increasing the number and height of fins to enhance electron mobility.
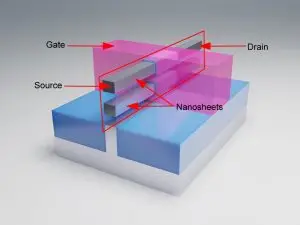
These limitations of FinFETs have pushed the semiconductor industry to find a way to accommodate more fins by stacking up horizontal sheets, leading to a new technology called gate-all-around FET. In a Gate-All-Around FET (GAAFET), the drain and source channels are stacked vertically. The vertically stacked channels are called nanosheets. By utilizing 2D and 3D transistor technologies, the drain and source terminals can be wrapped around the gate terminal in a gate-all-around FET. It is estimated that over 39 billion GAAFETs can be housed on a single IC.
How Does the Semiconductor Chip Shortage Impact Modern Life?
Semiconductors are at the center of modern life. Here are a few areas where semiconductors play a critical role:
Telecommunication
Semiconductors are vital to wireless communication by enabling electronic devices to deliver high Radio Frequency (RF) power. Advanced microchips, such as System On Chips (SOC) are deployed for 5G communication systems. Bluetooth connectivity, General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) tracking, and cloud storage are all made possible with semiconductors.
Automobile
The automobile industry is another sector that has benefited from semiconductor devices. Electric Vehicles (EVs), driver assistance system, air bag sensors, and cruise controls, are a few examples where semiconductor devices are deployed by the automotive industry.
Healthcare
The role of semiconductors in healthcare is indisputable. Semiconductors have changed the lives of millions through healthcare technologies such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines, blood sugar monitors, Electrocardiography (ECG) machines, and pacemakers.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Semiconductor devices, such as sensors, actuators, memory chips, and microprocessors, gave rise to IoT devices that connect and share data among devices that enabled smart homes, facial recognition, fingerprint detectors, and several other mind-boggling technologies.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has taken modern life to the next level. The groundbreaking AI technology trains a machine to reason, learn, and do things like a human brain would. Semiconductors are at the core of AI, which is integrated with many industries from automotive to healthcare. AI-powered machines help in automated manufacturing lines in many manufacturing industries. One of the many AI applications that got everyone talking is the chatGPT chatbot, which is a testimonial to the limitless capability of AI.
How are Companies Addressing the Global Semiconductor Chip Shortage?
While all the top-end semiconductor chip manufacturers are competing to create faster and more efficient microchips in the industry, the semiconductor chip shortage is a serious threat to the digital world. The end of the global shortage of semiconductor chips is not in sight due to high demand. This global shortage has impacted many industries and economies around the world.
The global semiconductor chip shortage peaked after the pandemic in 2019, as the use of electronics ramped up. The pandemic also disturbed the semiconductor raw material, semiconductor components, packaging materials, and equipment supply chains across the world. This interrupted the steady manufacturing of semiconductor chips. In addition, demands to fabricate complex chips with new materials, such as gallium nitride, for technologies like 5G networking and AI, are on the rise, slowing down the production time.
Many companies and governments are addressing this issue in many ways. Intel has planned to set up two new chip-making facilities in Arizona, investing $20 billion in this new project. Another major player in the semiconductor industry, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), has made plans to maximize silicon wafer production by investing $100 billion over the next three years. Not to mention the announcement of Samsung Electronics, the leading smartphone company, to invest over $151 billion by 2030 to meet semiconductor chip demands.
Semiconductor demand is driven by new applications that continue to push the limits of possibility to create a need for powerful processors and memory, which make the chip smaller and denser. Learn more about semiconductors with the THORS Semiconductor Basics course.

