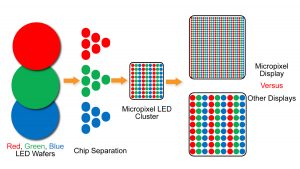
Course Description
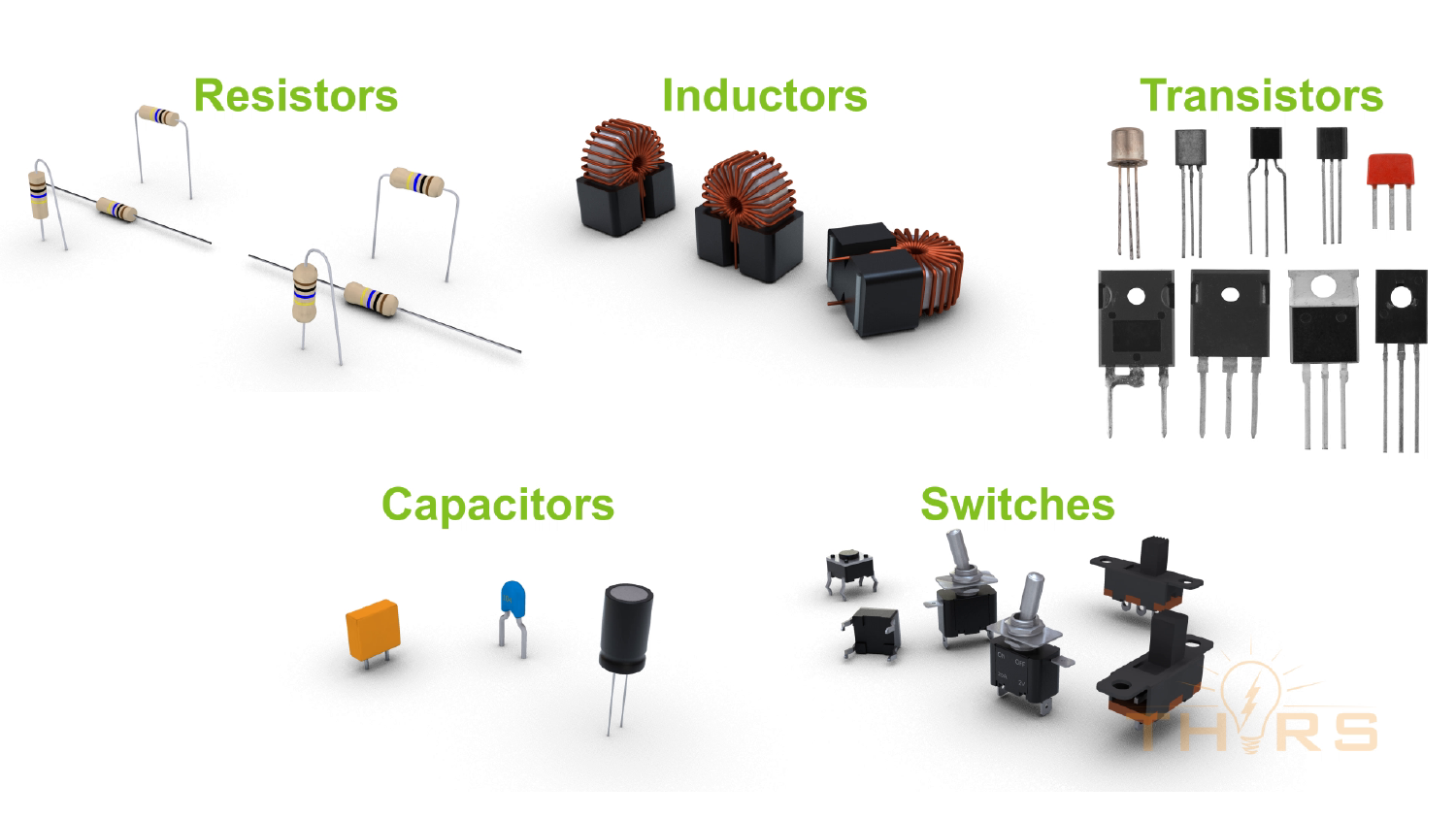
The evolution of electronics has propelled technological development forward. With the growing importance of electronics, there is also an increasing need for the knowledge of electronics and their application. The THORS Electronics Terminology course is created with the purpose to educate learners on the basic electronic components, working principles, electronic circuits, connectors, power converters, and its operation in a visually pleasing and highly interactive learning module.
Who will benefit from this Electronics course?
Quality, manufacturing, engineering, design, test, purchasing, and sales functions at organizations that require an understanding of basic electronics and electronic components.
Course Classification
*THORS uses the Bloom’s Taxonomy Methodology for our course development.
Certificate Awarded for Electronics Terminology

*upon successful completion
Related Posts

Comparing eLearning versus In-Person Learning
Introduction The world of education is rapidly changing, with technology playing an increasingly important role in the learning experience. One must take into account and

Developing Soft Skills in the Tech Industry
Soft skills in the tech industry, where precision and expertise are paramount, might seem secondary. However, soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, play

Enhancing Workforce Development with THORS eLearning Solutions
Workforce development programs are designed to equip employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in their roles and adapt to the evolving demands