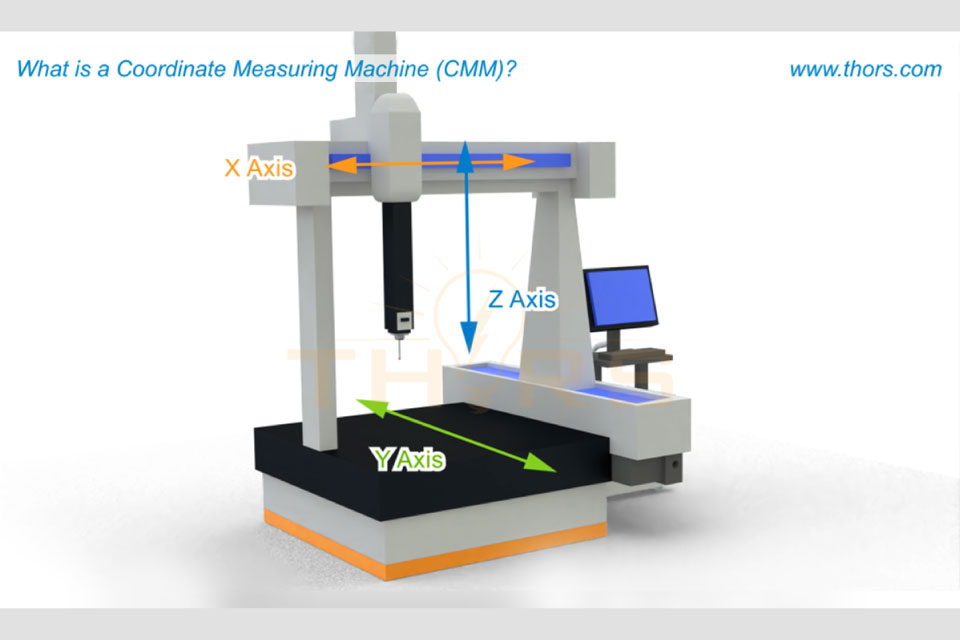
Inspection plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of a part. A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), being fully automated, enhances the inspection methodology by enabling quick and precise measurements. The THORS Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) Basics course illustrates the indispensable role of the CMM in the measurement world. Packed with graphics, the course will leave the learner with a valuable learning experience about the types of CMMs and the components of a CMM, as well as the measurement and reporting process of a CMM. Anyone working on a CMM machine including CMM Operators, Quality Engineers, Quality Managers, Design Engineers, and Manufacturing Engineers would benefit from this course.
The Learning Objectives for CMM Basics include:
- Recognize the advantages of using CMMs in coordinate metrology.
- Distinguish the types of CMMs and their applications.
- Identify the role of each CMM component in measurement.
- Understand the measurement process of a CMM and factors affecting the results.
- Examine the measurement analysis methodologies to evaluate the measured data.
- Learn the various forms of reporting data.
In addition to Learning Objectives, THORS utilizes Bloom’s Taxonomy Methodology in all of our courses. The methodology used in CMM Basics looks like this:
Finally, every course is fully outlined. Here is the outline for CMM Basics:
I. CMM Types and Components
A. CMM Types
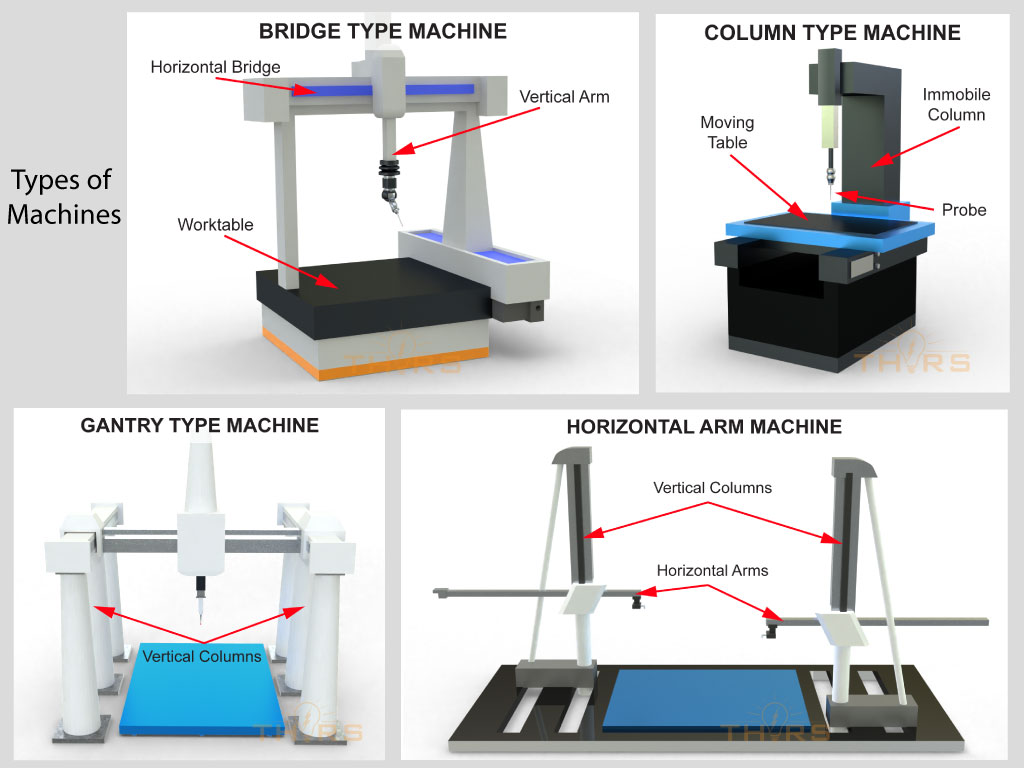
1. Bridge Type Machine
2. Horizontal Arm Machine
3. Gantry Type Machine
4. Column Type Machine
B. CMM Components
1. Probe Head
a. Fixed Probe Head
b. Articulated Probe Head
2. Probe
a. Contact Probe
i. Hard Probe
ii. Touch Trigger Probe
iii. Scanning Probe
iv. Surface Finish Probe
b. Noncontact Probe
i. Triangulation Probe
ii. Camera Probe
c. Hybrid Probe
3. Stylus
a. Stylus Construction
b. Stylus Combination
c. Stylus Shapes
d. Stylus Tip Materials
e. Stylus Contact Direction
4. Software
5. Accessories
a. Fixture
i. Dedicated Fixture
ii. Modular Fixture
b. Rotary Table
c. Air Cushion
II. Measurement Process
A. Alignment
1. 3-2-1 Alignment
2. Best Fit Alignment
3. RPS Alignment
B. Styli Calibration
C. Fixturing Strategy
D. Probing
E. Measurement Uncertainty
1. Measurement Uncertainty Importance
2. Measurement Uncertainty Causes
3. Measurement Uncertainty Reduction Methods
F. Stylus Compensation
G. Measurement Considerations
1. Thermal Influence
2. Other Influences
H. Measurement Analysis
I. Reporting Data
For more information on this course, please check out the course page for CMM Basics. This course is $180 and takes 2 learning hours.
Courses that relate to CMM Basics include Process Flow Diagrams, Control Plan, and Measurements: Basics Concepts.