Ball valves are highly versatile in design characteristics that make them suitable for transporting media of extreme natures. As a result, it is important to incorporate certain safety features in ball valves to prevent any hazard in the plant. Here are the most significant five safety features in ball valves.
What are Ball Valves?
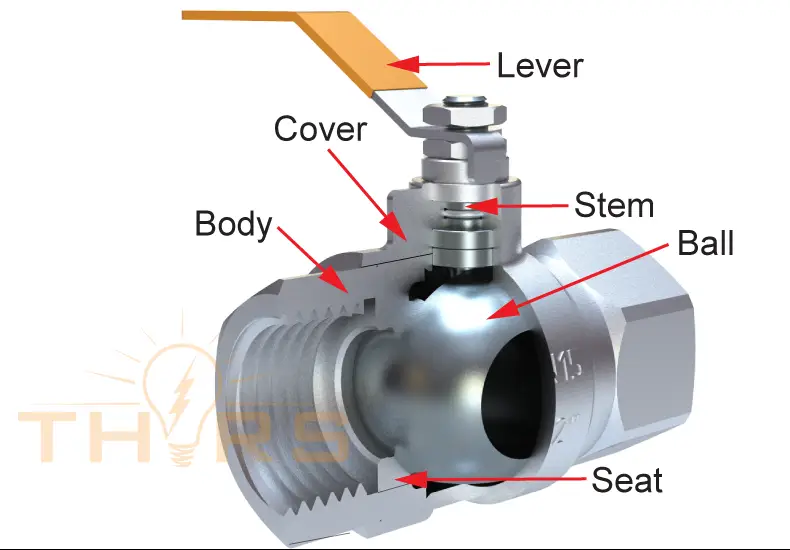
Ball valves are rotary motion valves with a ball, having a cylindrical through hole, as the closure member. Ball valves can be opened or closed by rotating the ball at a 90-degree angle on its axis. A ball valve is constructed of a body, cover, ball, seats, stem, and operator.
What are the Benefits and Application of Ball Valves?
Ball valves have high temperature and high pressure capabilities, and the use of stainless steel as a material of construction makes them ideal choices for combustible and corrosive applications. Further, ball valves give effective bubble tight shutoff making them a reliable choice in transporting dangerous gases. Ball valves are used to transport media in industries such as chemical, petrochemical, oil, and gas.
What are the 5 Safety Features in Ball Valves?
The safety features in ball valves are:
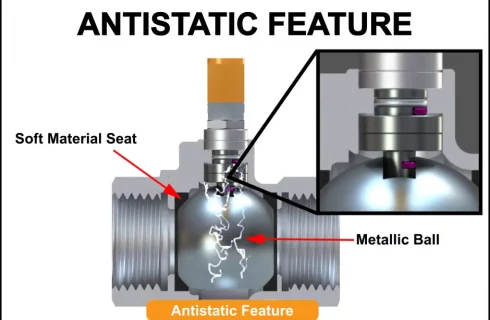
1. Antistatic Feature
Antistatic feature is a safety feature in ball valves to arrest the static charge generated by the contact between the metallic seat and the Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) seat. If the static charge produced in the valve is not contained, it could lead to a combustion with flammable media.
The antistatic feature is achieved by inserting devices called electrostatic spring sets between the ball and stem, and the stem and body to ensure that all metal valve parts are grounded. An electrostatic spring set is an assembly of a spring and a stainless steel ball.
2. Firesafe Feature
Firesafe feature is a safety feature in ball valves to minimize the leakage, in case of a fire in the pipeline.
The firesafe feature is achieved by incorporating a secondary metal sealing surface behind the primary PTFE seat.
In case of a fire in the pipeline, the soft seat may melt and become ineffective. In such a situation, the secondary metallic seat moves into action to provide a metal-to-metal seal, minimizing the leakage for an effective valve shutoff.

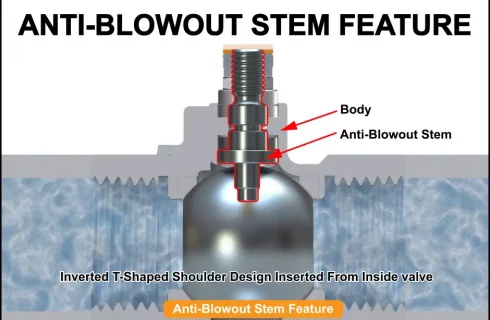
3. Anti-Blowout Stem
Anti-blowout stem feature is a safety feature to ensure that the stem is not pushed out of the valve’s body by the inline pressure. The anti-blowout stem feature is achieved by integrating an inverted T-shaped shoulder design for the stem that is then inserted from inside the valve’s body.
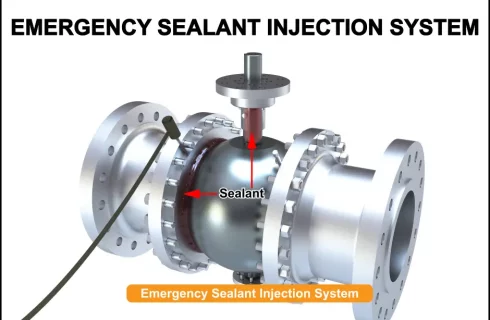
4. Emergency Sealant Injection System
Emergency sealant injection system is a safety feature in ball valves to provide sealing at both seats and the stem, in case of a leakage. Ball valves are fitted with a sealant injection mechanism, through which the sealant is injected to provide a barrier that minimizes leakage across the valve.
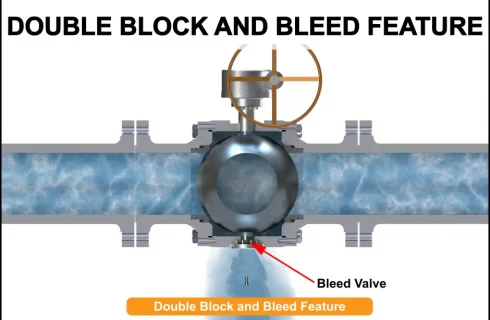
5. Double Block and Bleed Feature
Double block and bleed feature is a safety feature to achieve a definite shutoff in the ball valve to keep the process media away from the other equipment downstream. When a ball valve is turned off, the two pressure-energized seats act as two independent block valves, and the media in the cavity between the two seats is bled off using a bleed valve to release the pressure on the seats.
How Popular are Ball Valves?
Ball valves enjoy a large market share in the valve industry due to their diverse application. Moreover, with the advent of 3D printing, ball valves have found demands in the nuclear power sector as well. With all of these, the market share of ball valves, is projected to be at $16.2 billion by 2027. This has made it all the more essential for manufacturers to ensure the safety of ball valves. Enrich your knowledge about ball valves and other commonly used valves in THORS’ Valve Basics course to expand your knowledge in the field.