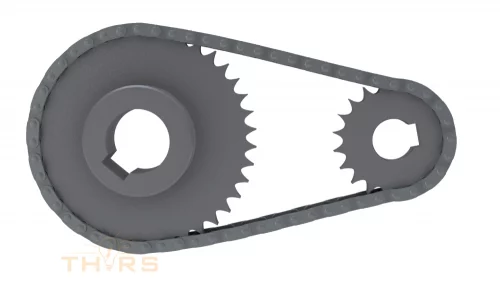
Course Description
The learning content in this industry library will help learners better understand the basic components, processes, types of chains, and a general terminology associated with industrial chains. These concepts are brought to life in these courses using realistic 2D and 3D models, helpful animations, and interactive quizzes. These courses are beneficial for those who are experienced in the industrial chain industry as well as those who are new to this industry.
Who will benefit from this industrial chains course?
Quality, manufacturing, engineering, designing, purchasing, and sales functions at organizations that require an understanding of industrial chains.
Course Classification
*THORS uses the Bloom’s Taxonomy Methodology for our course development.
Certificate Awarded for Chain Fundamentals: Industrial

*upon successful completion
Related Posts

A Differentiated Learning Approach: A Closer Look at THORS
In the wide landscape of learning methodologies, the pursuit of engaging and effective learning approaches has been ongoing. Among the myriad approaches, a differentiated learning

Boosting Employee Engagement in eLearning
Introduction In the realm of modern workplaces, boosting employee engagement in eLearning has become a pivotal factor in fostering productivity, job satisfaction, and overall organizational

Training Programs are Critical to Attracting and Retaining Talent
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, organizations face a unique set of challenges in finding, hiring, and retaining top talent. The tight labor market has