Differences Between Casting and Forging
In the world of manufacturing, few processes can match the intricate artistry and skilled precision of casting and forging, which do have a few differences. These age-old techniques have been refined over centuries, blending traditional craftsmanship with modern technological advancements. From intricate sculptures to automotive components, casting and forging have left a permanent mark on our world.
The Art of Casting
There are several differences between casting and forging. Let’s start with casting. Casting is an ancient technique that dates back thousands of years and has been used to create everything from decorative art pieces to industrial machinery components.
The Casting Process
- The casting process begins with the creation of a pattern, which is a replica of the desired part.
- This pattern is then used to make a mold, typically from sand, metal, or ceramic materials.
- Once the mold is prepared, molten metal is carefully poured into the cavity, allowed to cool, and solidified. The resulting casting is then removed from the mold, and any excess material is trimmed away. More information about the process can be found here.
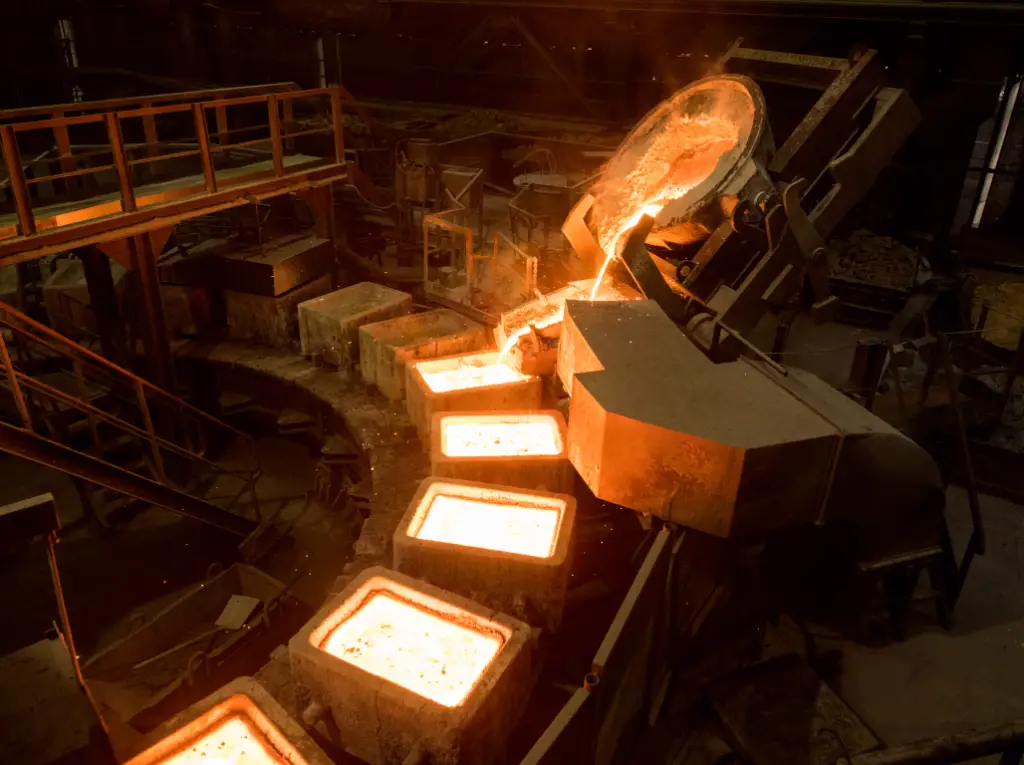

Excellence in Casting
The true beauty of casting lies in its versatility. Casting offers unparalleled flexibility in creating complex geometries and intricate details that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through other manufacturing methods. From the delicate details of a bronze sculpture to the intricate cooling channels within an engine block, casting allows for a level of craftsmanship that is unmatched.
One of the most impressive aspects of casting is the ability to work with a wide range of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, as well as advanced alloys and composites. This versatility has made casting an essential process in industries ranging from automotive engine blocks and cylinder heads to aerospace components, casting innovations are extensive and popular.
The Power of Forging
Forging, on the other hand, is a metalworking process that involves shaping and deforming metal through the application of compressive force. This technique dates back to the earliest civilizations and relies on the plasticity of metals, allowing them to be hammered, pressed, or squeezed into the desired shape without compromising their structural integrity.
The Forging Process
- The forging process typically begins with a billet or ingot of metal, which is then placed between two dies or hammers.
- Immense force is applied, causing the metal to deform and flow into the contours of the dies or hammer faces.
- This process can be performed using various methods, including hammer forging, press forging, and even advanced techniques like isothermal and precision forging.
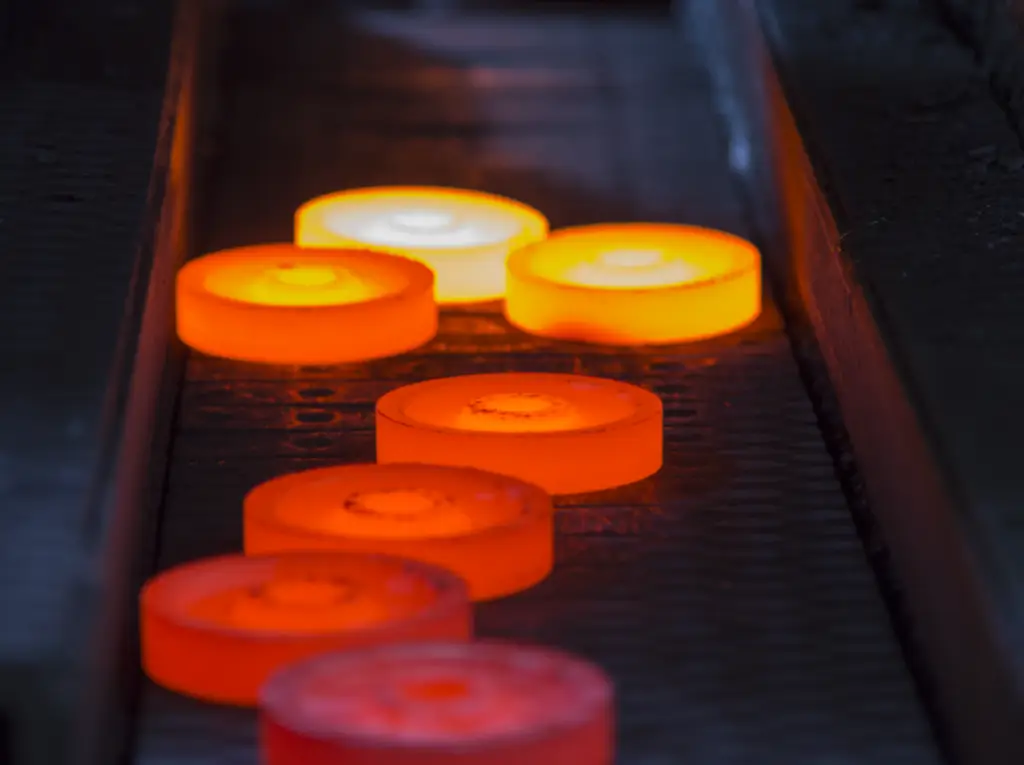

Excellence in Forging
One of the differences between casting and forging is that in casting, the material takes on the shape of the mold. Forging, on the other hand, involves manipulating the metal itself, altering its molecular structure, and enhancing its strength and durability. This process results in components with exceptional mechanical properties, making them ideal for applications that demand high and reliability.
The power of forging is a true testament to human ingenuity and skill. Experienced blacksmiths and metalworkers can transform a simple billet of metal into intricate shapes and forms, each hammer blow shaping the material with precision and finesse. From the delicate curves of a hand-forged sword to the massive components of a hydroelectric turbine, forging showcases the ability to bend and shape metal to our will.
Embracing Innovation
While casting and forging are deeply rooted in tradition, these industries have embraced innovation and technological advancements to enhance their capabilities and meet the ever-evolving demands of modern manufacturing.

Furthermore, the integration of automation and robotics has streamlined production processes, ensured consistent quality, and increased productivity, while also improving workplace safety and reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
As industries continue to evolve and demand increasingly complex and high components, the crafting excellence of casting and forging manufacturing will remain indispensable. These time-honored techniques, coupled with modern innovations, will continue to shape the future of manufacturing, enabling the creation of products that push the boundaries of design, performance, and durability. These processes not only create functional components but also serve as a canvas for artistic expression, blending form and function.