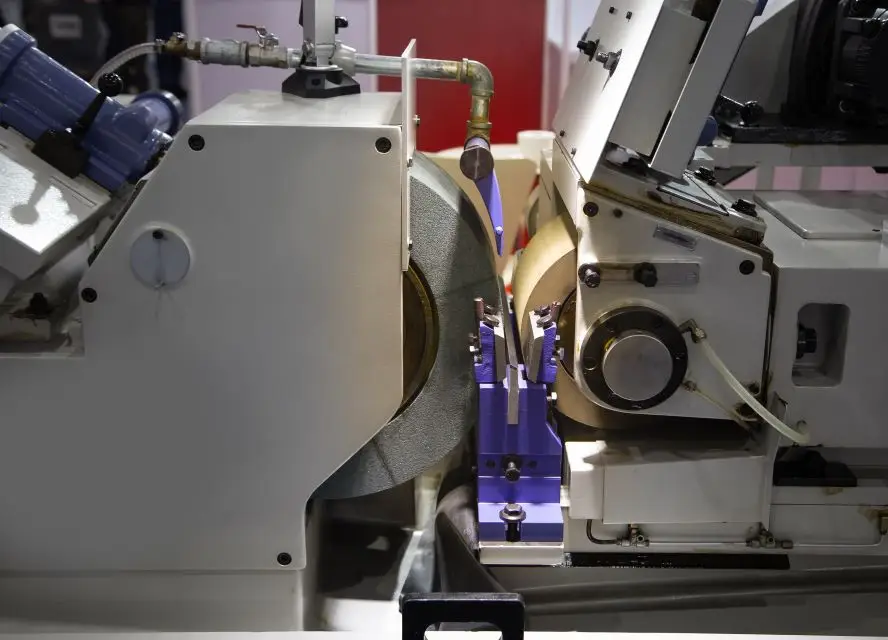
The synchronized movement of the two wheels in centerless grinding is important. The grinding wheel and the regulating wheel each has a specific role to play in achieving the desired outcome. Let’s explore the relationship between these wheels and how their coordinated movements drive efficiency and accuracy in the centerless grinding process. But first, watch our video about this process here.
The Grinding Wheel
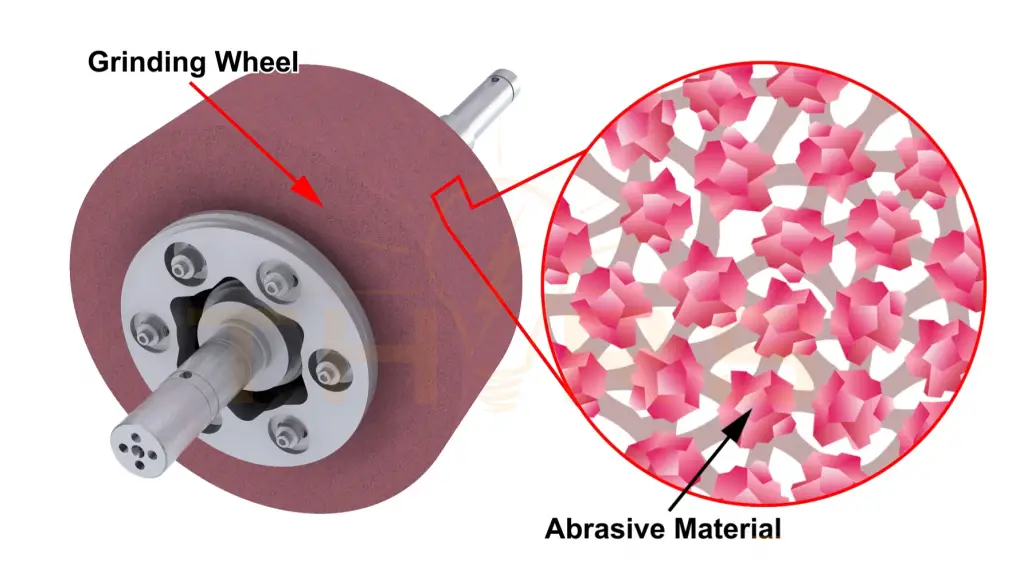
The grinding wheel in centerless grinding is the cutting tool that removes material from the workpiece. Composed of abrasive material bound together by vitrified bonds, the grinding wheel rotates at high speed, exerting controlled pressure on the workpiece to achieve the desired shape and surface finish. The grinding wheel’s rotation plays a pivotal role in ensuring precise cutting action and maintaining dimensional accuracy. The heat generated during grinding is efficiently managed using coolant, which prevents thermal damage to both the workpiece and the grinding wheel, ensuring prolonged wheel lifespan and consistent performance. Grinding wheels are periodically dressed, or dressed as needed based on wheel wear, to maintain their sharpness and effectiveness by removing worn abrasive grains and reshaping the wheel’s profile.
The Regulating Wheel
The regulating wheel in centerless grinding regulates the speed at which the workpiece rotates. It acts as a control wheel, which is crucial in the centerless grinding process. Composed of abrasive grains and held together by rubber bonding agents, regulating wheels are smaller in diameter and operate at a slower speed than the grinding wheel. Regulating wheels may also undergo dressing in certain situations to maintain optimal performance, although it is less common than dressing grinding wheels.
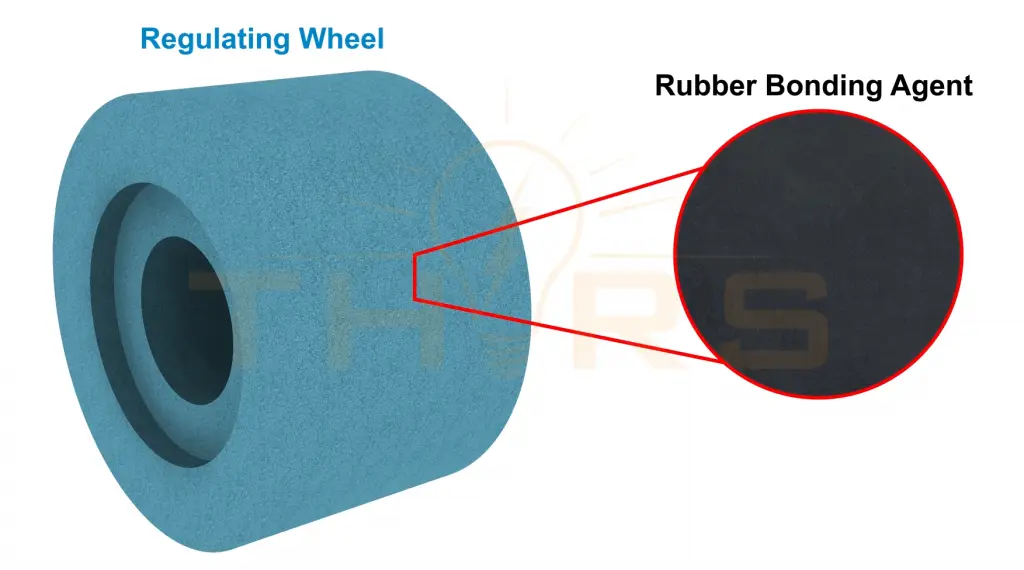

Achieving Balance in Movements
In centerless grinding, achieving a precise balance between the grinding and regulating wheels is crucial for optimal performance. The grinding gap, the space between the two wheels, must be accurately calibrated to accommodate the workpiece while ensuring stability and control. Proper synchronization between the wheels ensures consistent material removal and prevents deviations or irregularities.
Parameters such as wheel speeds, feed rates, and grinding forces are essential to balance their interactions. Adjusting these parameters ensures smooth material removal, optimal surface integrity, and minimal workpiece deflection. Proper balance also reduces vibration and wear on the wheels, enhancing the overall efficiency and accuracy of the grinding process.
Modifying any one parameter, such as the grinding wheel speed necessitates corresponding adjustments in the feed rate and regulating wheel speed to maintain balance. Ensuring these adjustments are synchronized is critical for achieving the desired grinding performance and maintaining overall process stability.
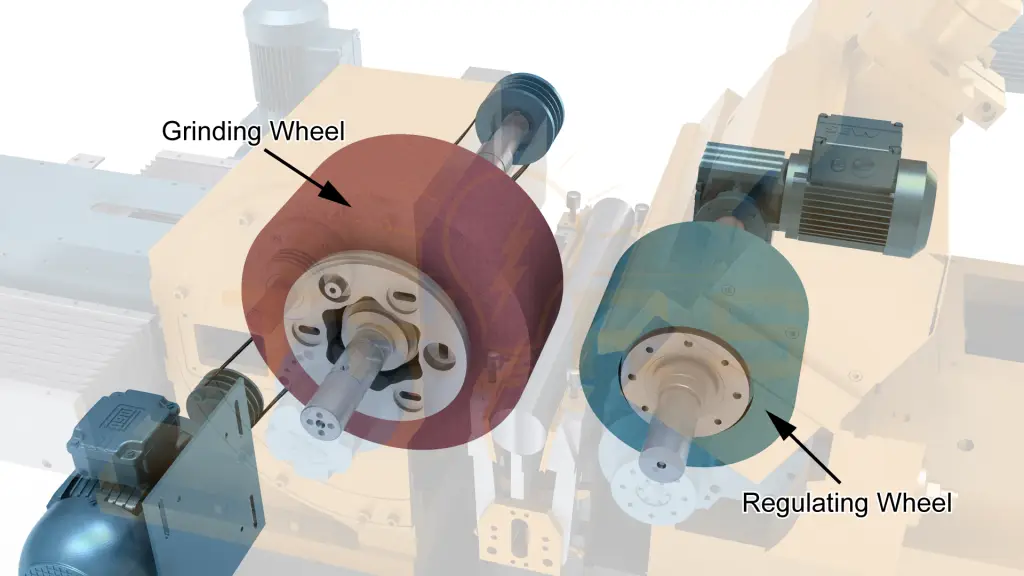
Enhancing Efficiency and Ensuring Consistency
The coordinated efforts of the grinding and regulating wheels enhance the efficiency of the centerless grinding process. By optimizing wheel speeds, feed rates, and grinding parameters, manufacturers can achieve higher throughput and reduce cycle times.
Beyond efficiency, the collaboration between the grinding and regulating wheels ensures consistency and reliability in the manufacturing process. Their synchronized movements maintain tight tolerances, smooth surface finishes, and precise geometries, ensuring that each workpiece meets stringent quality requirements. This consistency is essential for producing high-quality components that meet customer expectations and industry standards.
Consequences of Imbalanced Wheels
When the grinding and regulating wheels lose balance, the consequences are significant and immediate, which could cause serious safety issues to personnel and equipment. The accuracy and quality of the finished components can also be effected in these ways:
- Variation in part dimensions
- Surface irregularities
- Out-of-round workpieces
Additionally, imbalanced wheels can cause excessive heat generation, leading to thermal damage in the workpiece. The increased vibration and strain on machine components can accelerate mechanical wear and tear, requiring frequent maintenance and repairs.
Prioritizing proper wheel balance and alignment is essential for maintaining consistent product quality and prolonging the lifespan of equipment while ensuring a safe working environment for personnel.
In conclusion, understanding the roles of each of the wheels used in centerless grinding, and how they work together is essential for achieving precision, accuracy, consistency, and efficiency with the centerless grinding process.
Would you like to learn more? Check out our THORS Academy courses, Centerless Grinding I and Centerless Grinding II.