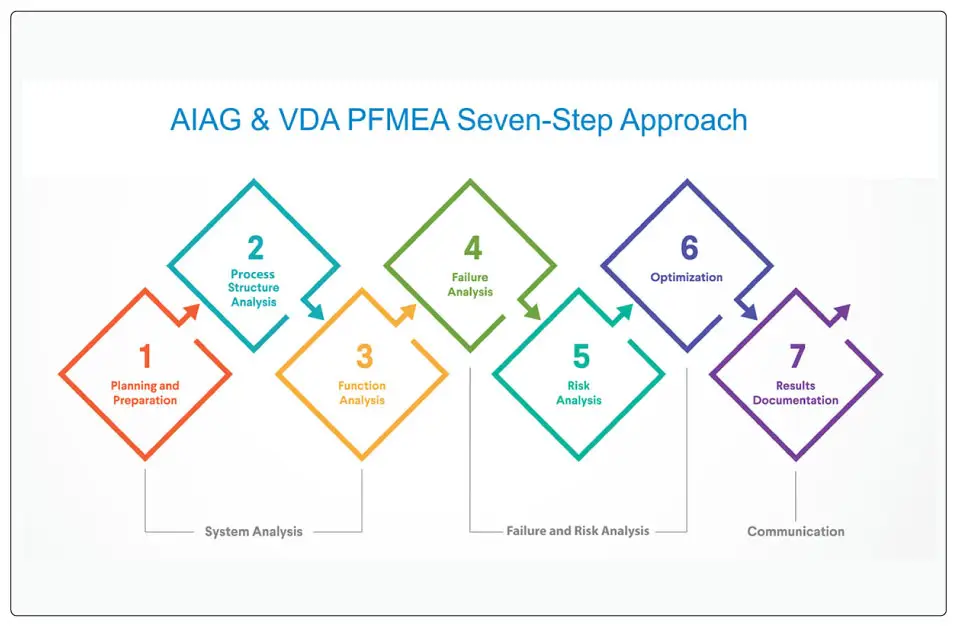
In 2019, the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) and Verband der Automobilindustrie (VDA), or the German Association of the Automotive Industry, combined their expertise to develop the AIAG & VDA PFMEA seven-step approach for process control.
Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is a structured approach used to identify and prioritize potential failure modes in a process, product, or service, and to understand their potential effects.
The seven steps in the AIAG & VDA PFMEA seven step approach and methodology are planning and preparation, process structure analysis, function analysis, failure analysis, risk analysis, optimization, and results documentation.
Step 1: Planning and Preparation
Planning and preparation is the first step in the AIAG & VDA PFMEA development where the process sequences are determined for the new product realization. This step enables the organization to focus its resources on the process steps.
The planning and preparation step helps the team with project identification and making the project plan based on the customer requirements. This step also helps the team in defining the when, what, who, and how for each activity and defining the inputs for the process.
Step 2: Process Structure Analysis
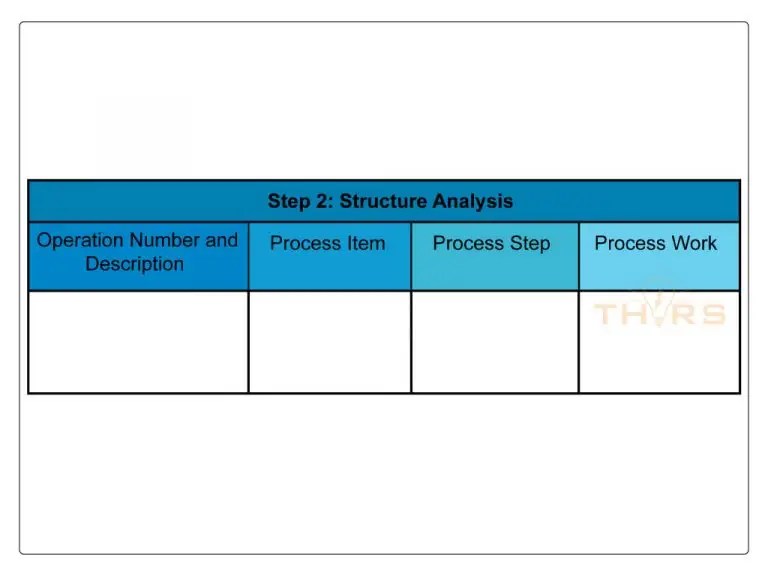
Process structure analysis is the second step in the AIAG & VDA PFMEA seven-step approach. In this step, the multidisciplinary team fragments the manufacturing system into a structure tree that identifies the process items, process steps, and work elements (4M).
Process structure analysis helps the multidisciplinary team with the visualization of the scope of analysis, creation of the Process Flow Diagram (PFD), identification of the process steps and sub-steps, and creation of a basis for the next step.
Step 3: Function Analysis
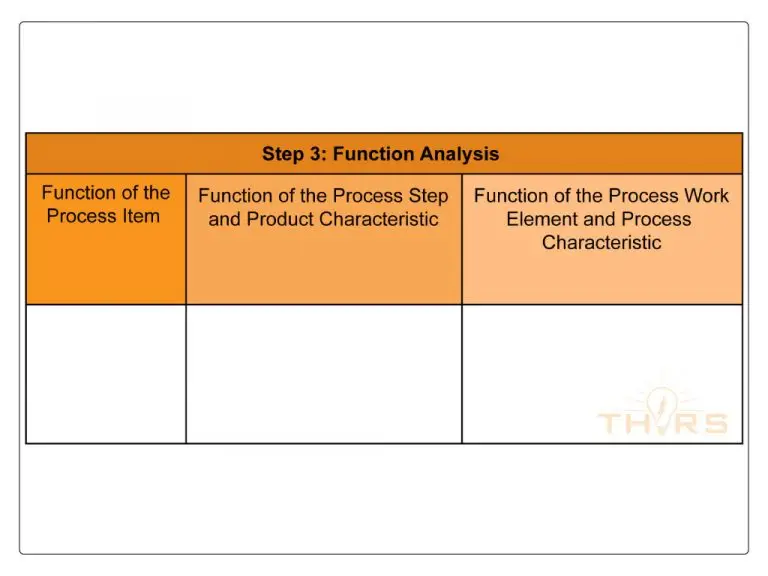
A function analysis is the study of what each process step is intended to do. A process step may have more than one function and the function may include the performance requirements. Product functions are understood from the product drawings and specifications.
A function analysis ensures that the intended functions and requirements of the product as well as the process are appropriately allocated. Further, it helps the multidisciplinary team with the visualization of the product and process functions, preparation of the function tree, linkage of characteristics to the functions, interaction between engineering teams, and serves as a basis for failure analysis, which is the next step.
Step 4: Failure Analysis
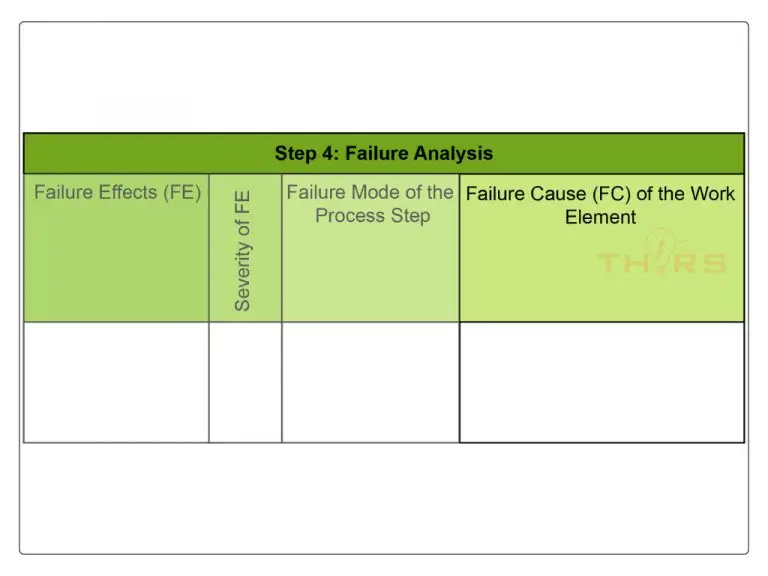
Failure analysis is the step to identify failure effects, failure modes, and failure causes in a process to depict their relationship with risk assessment. Failure analysis must be performed for each element or step in the process description. Examples of process failure include:
- Nonconformities
- Inconsistency or partially executed tasks
- Unintentional or unnecessary activity
It also helps to establish a link between the customer and the supplier to assess the failure impact and to enable the documentation of failures in the PFMEA form sheet.
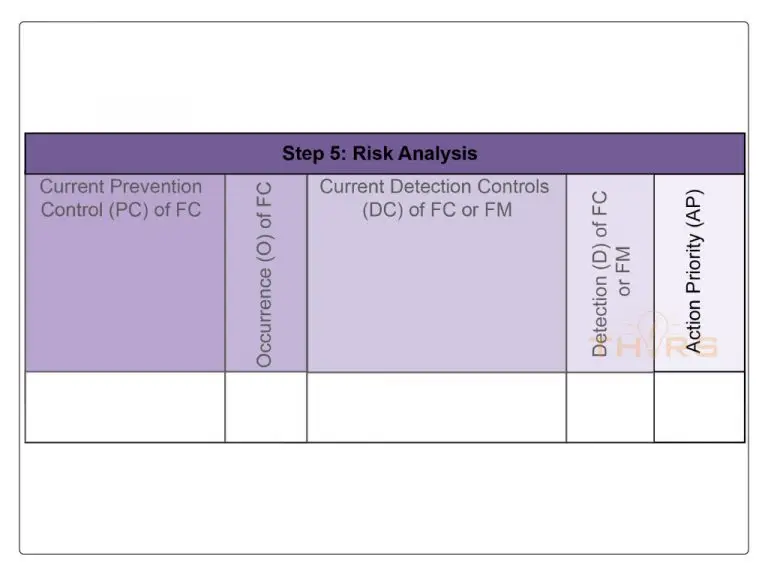
Step 5: Risk Analysis
Risk analysis is the process of eliminating risk by evaluating severity, occurrence, and detection with the aim of prioritizing the need for actions to reduce or eliminate the risk.
Risk analysis helps with the evaluation of existing controls, planned controls, rating of failures or potential failures, assignment of prevention controls to the failure causes, assignment of detection controls to the failure causes, failure modes (or both) rating of severity, occurrence, detection for each failure chain, and evaluation of action priority and optimization.
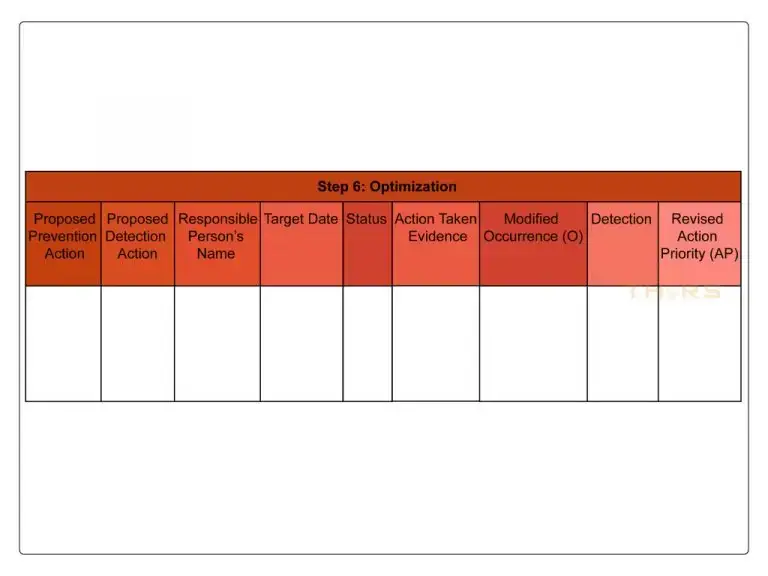
Step 6: Optimization
The purpose of process optimization is to determine and implement actions to reduce or eliminate risk and to assess the effectiveness of these actions. The end result is one that minimizes the risk of producing and delivering products that do not meet the expectations of the customer and stakeholders.
Optimization helps with the identification of preventive actions to reduce or eliminate risks, defining responsibilities and targets for implementation. It also helps with re-assessment and documentation of risk after the actions are taken, and the percolation and communication of potential failures among customers, suppliers, management, and production line employees.
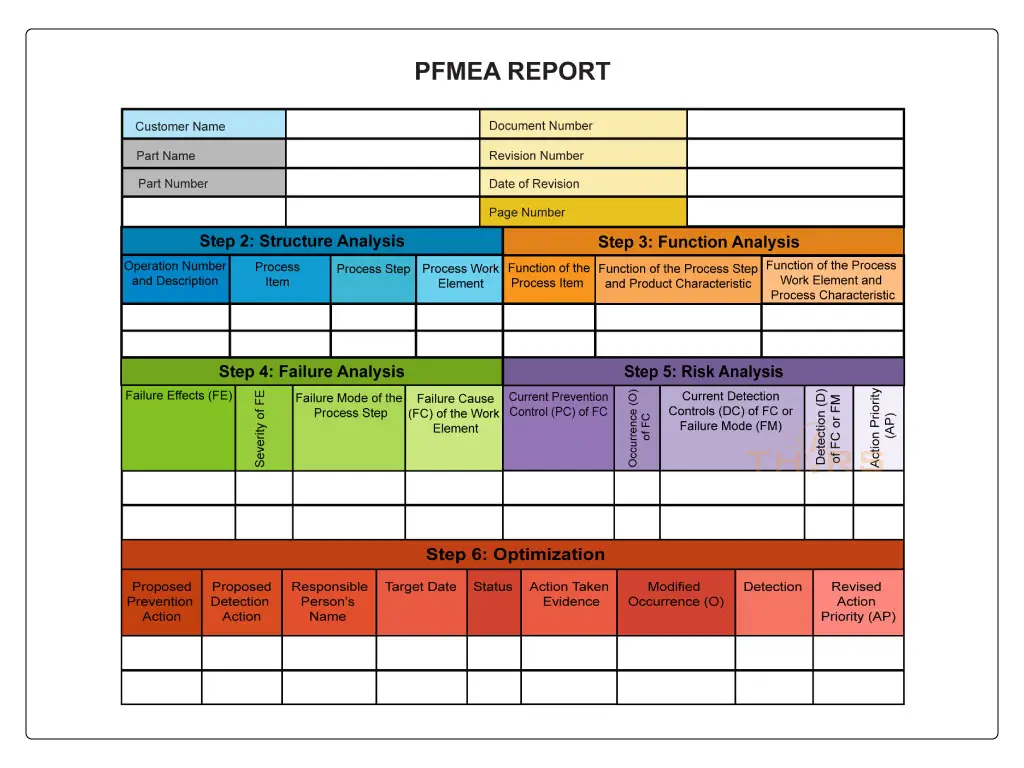
Step 7: Results Documentation
Results documentation, the final step in the AIAG & VDA PFMEA seven-step approach, is the communication of the summary of the PFMEA activity. Results documentation includes the results and conclusions of the analysis within the organization as well as with the customers or suppliers based on the intellectual property agreements. The documentation must contain the actions taken to reduce the risks and also the verification of the effectiveness of the actions. The documentation can be in the form of a PFMEA report.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the AIAG & VDA PFMEA Seven-Step Approach presents a systematic and comprehensive methodology for risk analysis, essential in today’s complex manufacturing environments. This approach not only enhances understanding but also ensures a proactive stance in identifying and mitigating risks during product development. To gain a deeper insight into this crucial process and to master its application, we invite you to access our course, Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) AIAG & VDA. This course is designed to provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively implement this advanced approach in your organization. Enroll now and take a significant step towards mastering risk analysis and ensuring product quality and safety.