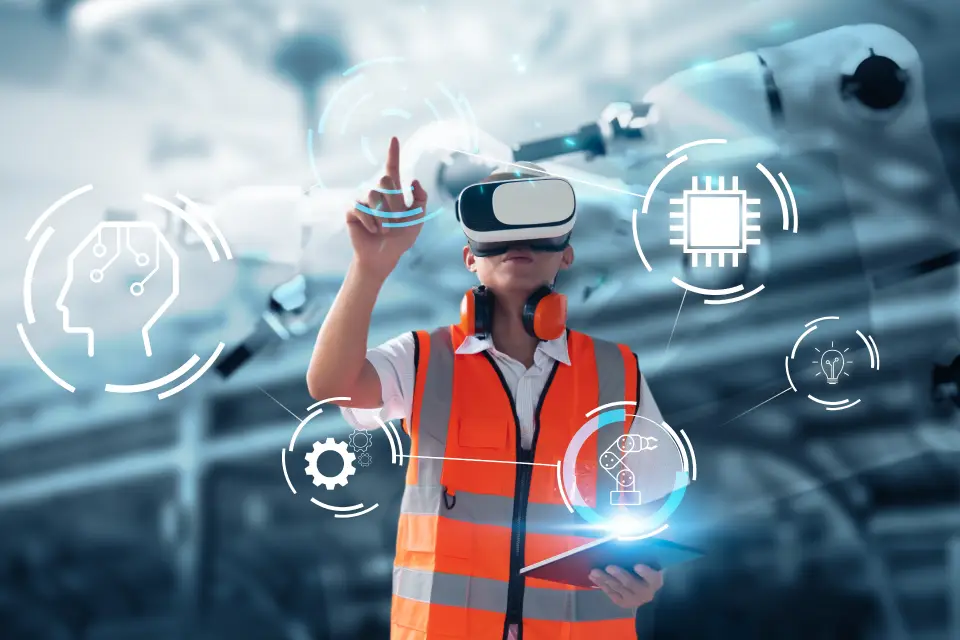
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology and industry, virtual reality (VR) in technical training is leading a revolutionary transformation in how professionals are trained. Virtual Reality offers immersive, interactive, and highly effective training experiences. Here’s a closer look at the role of VR in technical training and its potential to reshape the future of workforce development.
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual reality refers to a technology that uses computer-generated environments to simulate physical presence in real or imagined worlds. It typically involves wearing a VR headset that provides immersive visuals and audio, allowing users to interact with and realistically navigate through these virtual environments.
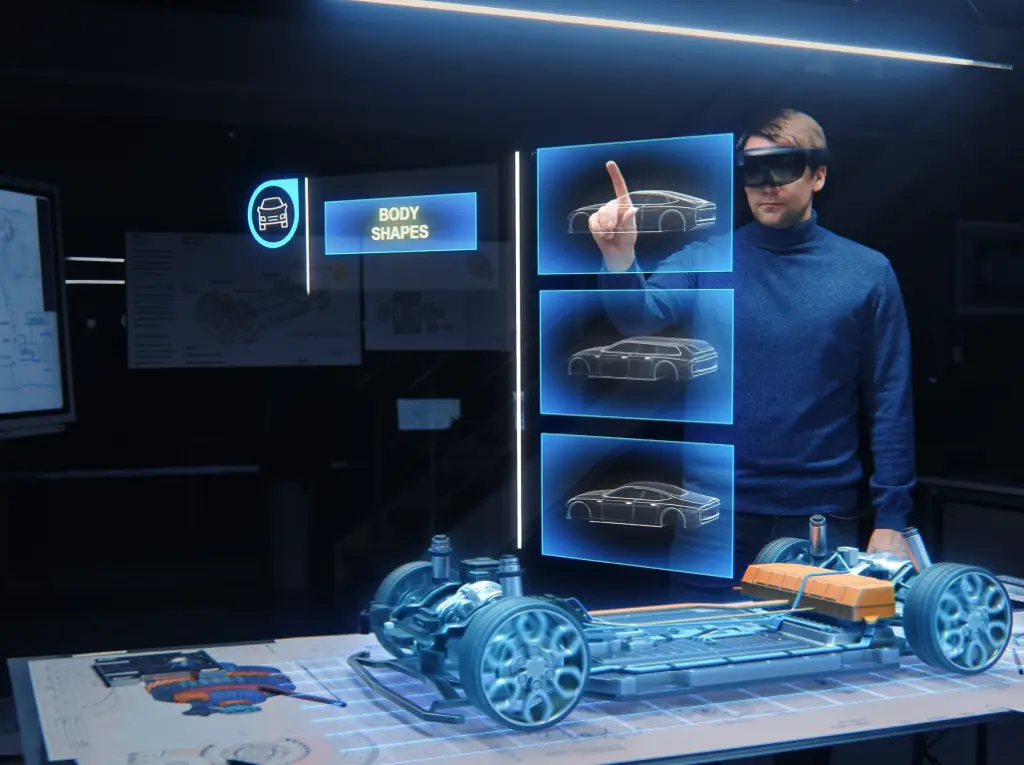
Virtual Reality Example: Simulating Car Assembly for Manufacturing Training
Imagine a car manufacturing company using VR to train assembly line workers. By wearing VR headsets, new employees can be fully immersed in a virtual factory floor where they learn how to assemble car components.
The VR simulation accurately replicates the real assembly process, enabling trainees to interact with virtual machinery, tools, and parts. They can practice tasks like installing engine components, connecting wiring harnesses, and inspecting finished products, all within a safe and controlled virtual environment. Virtual reality transforms technical training by immersing trainees in realistic, computer-generated environments that simulate real-world scenarios.

How Does Virtual Reality Work in Technical Training?
Here’s a detailed look at how VR operates:
- Immersive Simulation: VR headsets are used to create immersive simulations of environments relevant to the training objectives. For example, in manufacturing, VR can replicate factory floors, equipment setups, or hazardous scenarios.
- Interactive Experience: Trainees interact with the virtual environment using controllers or other input devices. They can manipulate virtual objects, operate machinery, or perform tasks like those required in their actual job roles.
- Realistic Feedback: VR provides real-time feedback based on trainees’ actions. For instance, if a trainee is learning to operate a complex machine, VR can simulate the machine’s response to their actions, such as starting up, adjusting settings, or detecting errors.
- Hands-On Learning: The hands-on nature of VR allows trainees to practice procedures repeatedly until they master them. This active learning approach enhances skill development and retention compared to passive learning methods.
- Safety and Risk Mitigation: VR training eliminates risks associated with traditional methods, such as operating dangerous machinery or handling hazardous materials. Trainees can make mistakes in the virtual environment without consequences, promoting a safe learning experience.
- Advanced Analytics: VR platforms often include analytics capabilities that track trainees’ performance metrics. The integration of advanced analytics into VR platforms enhances the effectiveness of technical training by providing valuable data-driven insights into trainees’ performance and learning progress.
How Welcomed Is VR Technology Among Trainers in Technical Training?
Trainers in technical training are increasingly embracing VR technology for its ability to create immersive learning experiences that engage trainees deeply. It offers a unique opportunity to practice skills in realistic virtual environments, enhancing learning retention effectively. Beyond traditional methods, VR enables trainers to deliver consistent and cost-effective training experiences across different locations. Despite initial challenges such as implementation costs and learning curves, trainers recognize VR’s potential to innovate training methodologies and significantly improve learning outcomes.
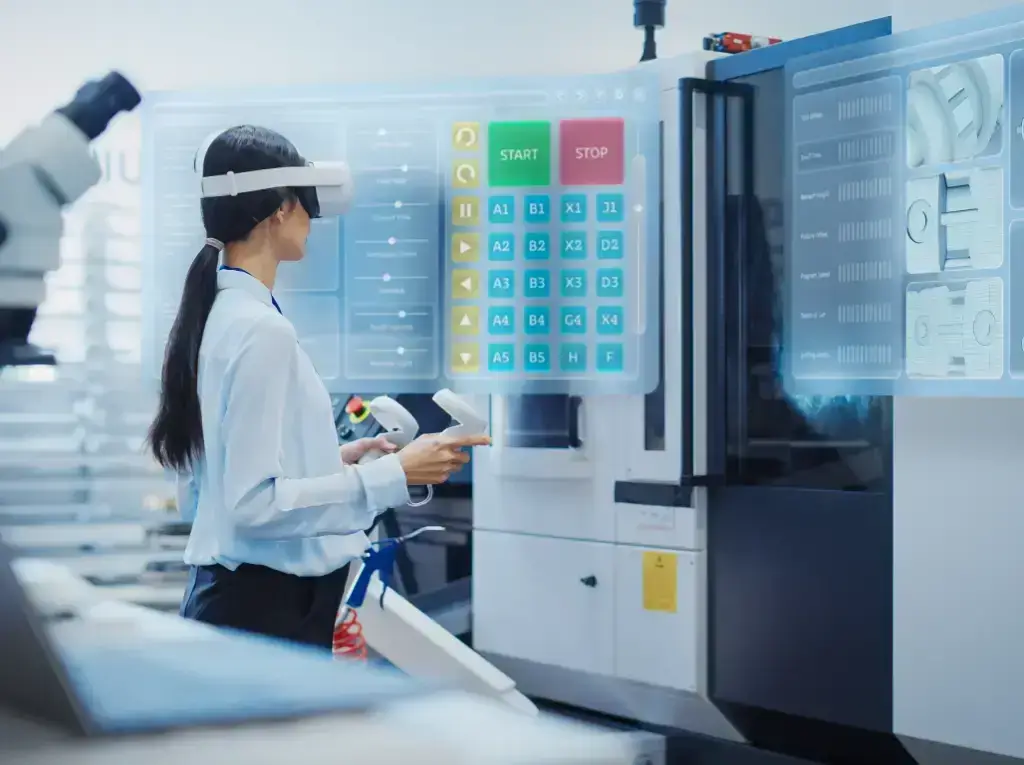

Future Outlook
The future of virtual reality in technical training looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology. As VR hardware becomes more affordable and accessible, its adoption across various industries is expected to grow. Additionally, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) with VR will further enhance training programs, offering personalized learning experiences and adaptive training modules.
Innovations such as haptic feedback, which provides tactile sensations, will make VR training even more realistic. Trainees will be able to feel the texture of materials, the resistance of objects, and the impact of actions, adding another layer of immersion and realism to the training experience.



