Safely handling Lithium-Ion batteries is important. These batteries power everything from cellphones to Electric Vehicles (EVs). The lithium-ion battery’s efficiency, lightweight design, and great energy capacity make them appealing. However, poor handling or storage can result in major safety hazards including overheating, fires, and even explosions.
In this blog post, we’ll go over ten essential tips for safely handling lithium-ion batteries. Following these practical instructions can preserve the longevity of the lithium-ion batteries and reduce potential hazards.
1. Avoid Physical Damage
Lithium-ion batteries must be handled cautiously to prevent physical damage, as crushing or dropping the battery can compromise its internal structure, potentially leading to leaks, fires, or even explosions. Proper handling and storage are critical to maintaining battery safety.

2. Use Approved Chargers
Using the incorrect or non-approved charger can cause overcharging, which generates and raises the danger of fire or battery damage. To ensure safe charging, always use a charger specifically designed for the battery.
3. Store Properly
Batteries can overheat or degrade more quickly if stored in severe temperatures or under direct sunshine. A cool, dry environment free of extreme heat and humidity is ideal for storage. This helps to extend battery life and prevents safety issues.
4. Check for Damage
Lithium-ion batteries should be inspected for problems, such as swelling, leaks, cracks, or obvious wear, before being used or charged. A battery is dangerous to use and needs to be disposed of properly if it exhibits any of these symptoms.
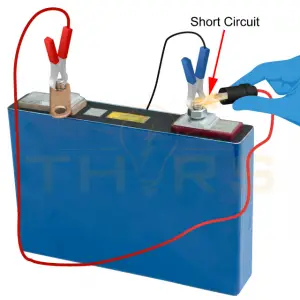
5. Avoid Short Circuits
When a battery’s positive and negative terminals come into contact with one another, a short circuit happens, which may result in a spark or fire. In order to avoid unintentional short circuits, keep batteries away from metal things like coins or keys. For extra security, use cases or protective covers.
6. Stay within the Optimal Charging Range
Lithium-ion batteries perform best when charged between 20% and 80%. Charging to 100% on a regular basis might diminish its life. To ensure the optimum performance and longevity, charge and drain your battery within this range.
7. Don’t Mix Old and New Batteries
When using numerous battery cells together to create batteries, such as in a laptop, avoid combining old and fresh battery cells. Different charge levels or ages of a battery cell might produce uneven discharge, resulting in a malfunction or failure. Always utilize battery cells with similar ages and charge levels in a battery.
8. Transport with Care
Batteries are susceptible to short circuits and damage when being transported, particularly when in high quantities. Batteries should be kept in their original container provided by the manufacturer or wrapped with nonconductive materials such as foam or plastic to lower this risk. Batteries should never be carried free in pockets or bags where they could meet metal items.
9. Dispose Properly
Lithium-ion batteries should never be discarded without following the universal guidelines. Lithium-ion batteries include chemicals and metals that, if not disposed of appropriately, can be harmful to the environment. Take them to a recognized facility to ensure that they are safely disposed.
10. Monitor Battery Heat
A lithium-ion battery malfunction could result in a fire or explosion if it becomes too hot while being used or charged. Normal use should only cause batteries to warm up little. Stop using them if they get too hot, let them cool, and replace them if needed.
Lithium-ion batteries are crucial for powering today’s technological devices, but they must be handled with care to ensure safety. After reviewing the THORS Course on Lithium-Ion Battery Safety you will be able to:
- Identify common noncritical battery hazards such as heavy battery lifting, water ingress, high magnetic field, and high current.
- Recognize the critical battery hazards such as cell venting, electric shock, arc flash, and fire.
- Describe the importance of a robust Battery Management System (BMS), Manual Service Disconnect (MSD), and High Voltage Interlock Loop (HVIL) for safe battery operation.
- Explain the proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for electric shock and arc flash.
- Understand safe battery transportation requirements to ensure safe handling.
Remember that safety is a shared responsibility. Following each of these ten tips is just the beginning.


