Introduction
In recent times, precision engineering with robotics continually reshapes the manufacturing industry’s paradigms. Among these advancements, the role of robotics plays a key factor in influencing modern manufacturing processes’ efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Robotics is a vital tool in manufacturing, from complex electronics manufacturing to automotive assembly lines, to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced markets.
Precision Engineering in Robotics
Precision engineering with robotics focuses on designing, manufacturing, and assembling components with extremely high levels of accuracy and consistency, and robotics has revolutionized the way precision engineering is achieved. The pursuit of robotics in precision engineering not only enhances the performance and reliability of these products but also enables manufacturers to achieve higher levels of precision, efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Robotic arms equipped with advanced sensors and actuators can perform tasks with micron-level accuracy, ensuring that each component is manufactured to exact specifications. Whether it’s welding, painting, or assembling intricate parts, robots excel in repetitive tasks with unparalleled precision, minimizing defects and waste in the production process.
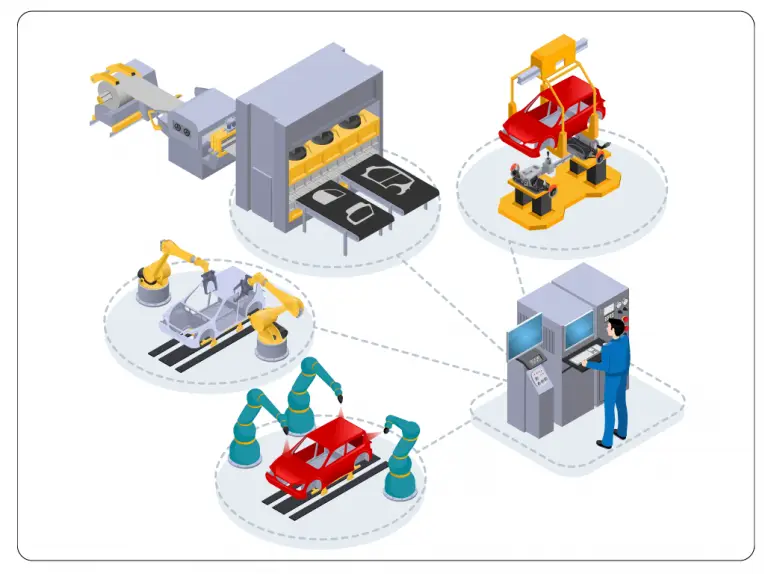
Safety in Manufacturing
Safety engineering is applying scientific and engineering principles to identify and mitigate potential hazards, prevent accidents, and minimize risks in industrial facilities and public spaces. The role of robotics also extends to ensuring workplace safety of humans, equipment, and the manufacturing environment. Collaborative robots, also known as cobots, are being used more often in factories sharing workspace with human laborers to enable smooth communication and teamwork.
Modern-day robots are built with safety features such as collision detection sensors, emergency stop mechanisms, and protective barriers, minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries on the factory floor. Robots also excel in handling hazardous materials and operating in environments with high temperatures, toxic fumes, or other adverse conditions that may pose health risks to human workers. This proactive approach not only safeguards their employees but also mitigates potential liabilities associated with workplace accidents.
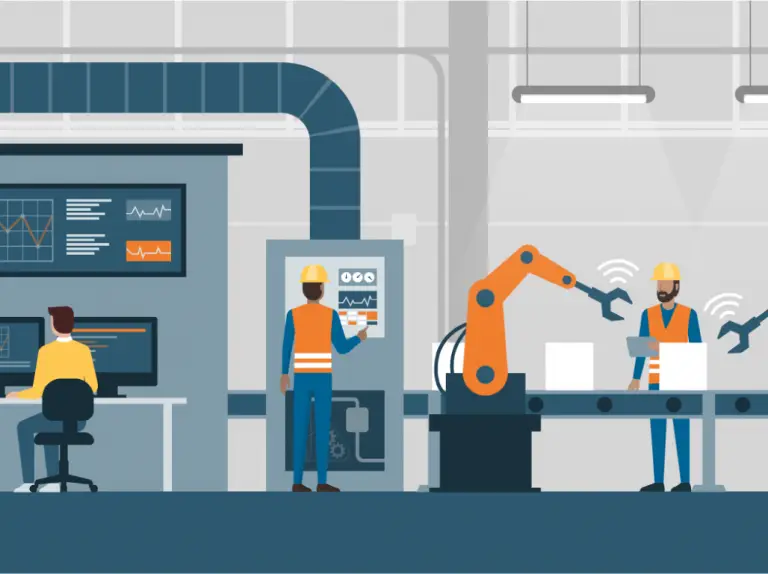

Conclusion
With the emergence of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT), the role of robotics is evolving to become an integral part of modern manufacturing systems. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, allows the robots to make data-driven decisions, learn from experiences, and adapt to changes in the environment. Embracing technological advancements enables manufacturers to stay competitive in a rapidly changing global marketplace.