Course Description
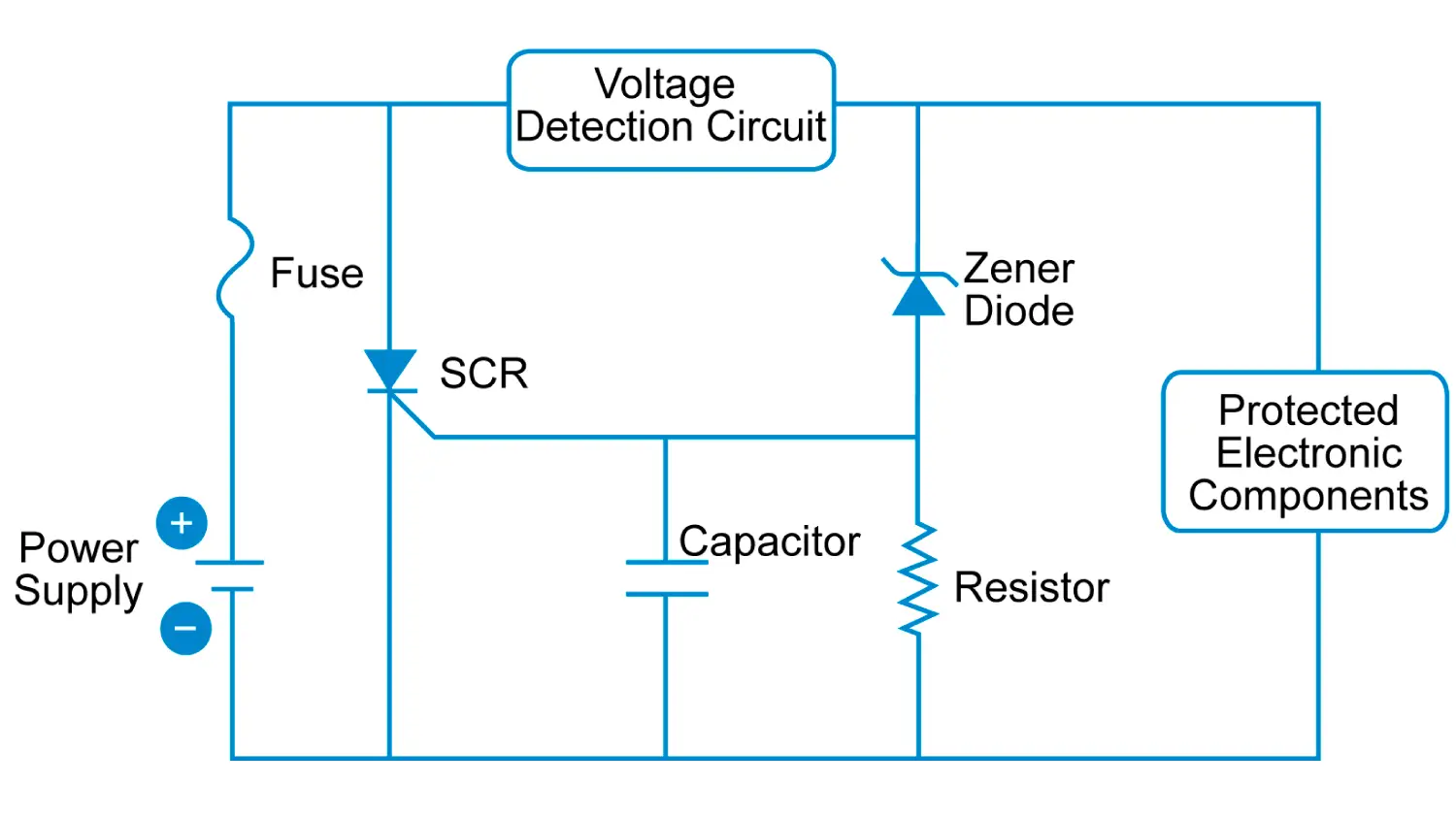
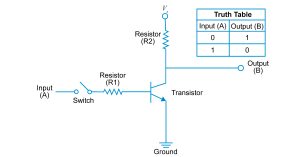
The THORS Active Electronic Circuit Basics course focuses on electronic circuits that can be built using active electronic components, such as transistors. This course covers power converters that are built using active electronic components, such as a diode or Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR). Power converters classified based on the power conversion method and the power supply design are also discussed in detail. Interactive quizzes are integrated to enhance the learning experience by allowing learners to assess their comprehension of the visually stimulating content.

Who will benefit from this active electronic circuit course?
Quality, manufacturing, engineering, design, test, purchasing, and sales functions at organizations that require an understanding of basic electronics and electronic components.
Course Classification
*THORS uses the Bloom’s Taxonomy Methodology for our course development.
Certificate Awarded for Active Electronic Circuit Basics

*upon successful completion
Related Posts

Top 5 Applications of Sealed Connectors in Wiring Harnesses
Sealed connectors in a wiring harness are protective components designed to prevent environmental contaminants such as water, dust, and chemicals from compromising electrical connections. The
Semiconductor Chip Shortage Significance
In an increasingly interconnected world driven by technological advancements, a looming crisis has captured the attention of industries, governments, and individuals alike: the semiconductor chip

Semiconductor Metrology Instruments: 8 Trends and Their Advantages
The semiconductor metrology instrument industry has been constantly evolving due to semiconductor miniaturization and the pursuit of higher performance to create more and more powerful