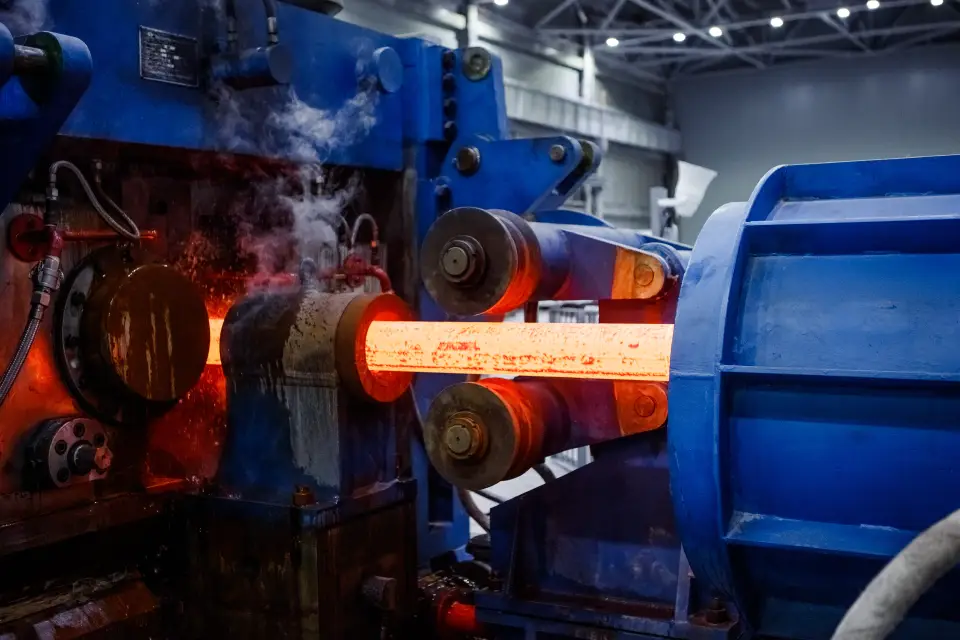
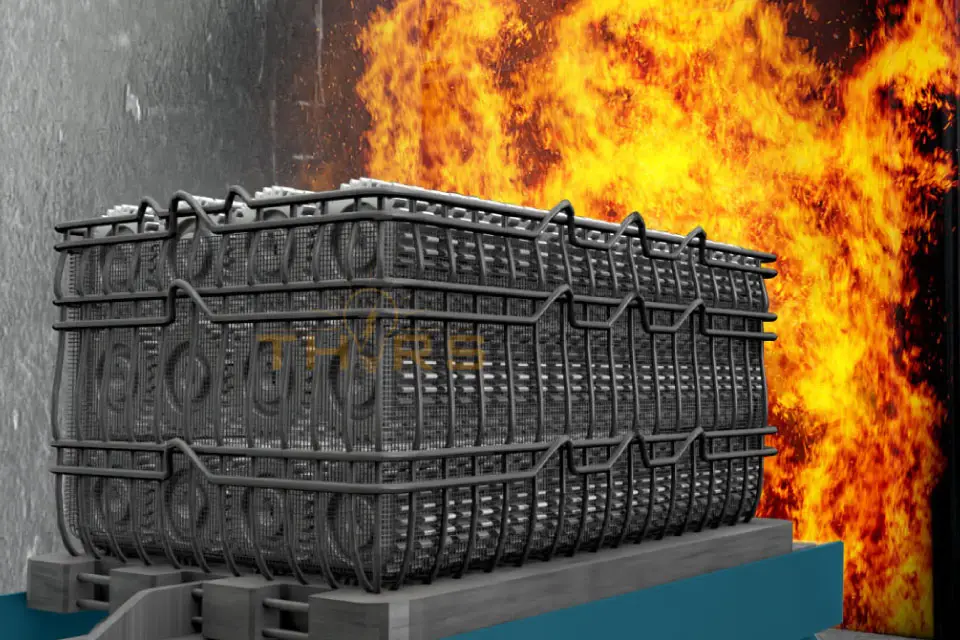
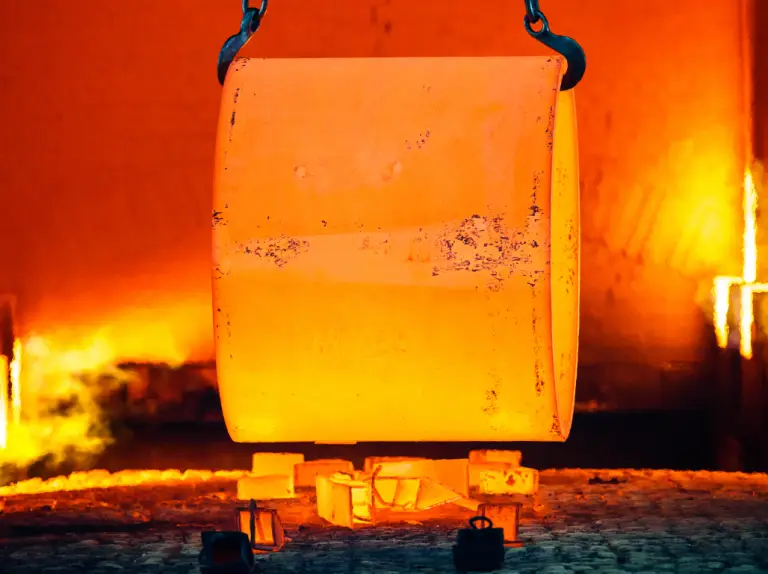
Heat treatment in manufacturing is a process used to modify the physical and sometimes chemical properties of materials, typically metals or alloys. Through controlled heating and cooling cycles, heat treatment optimizes the material’s characteristics to meet specific performance requirements.
Why Heat Treatment?
By subjecting metals or alloys to controlled heating and cooling cycles, the microstructure of the material is altered, resulting in improvements in hardness, strength, toughness, and ductility. This process also helps to relieve internal stresses, reducing the risk of distortion or failure in the finished components. Heat treatment in manufacturing is a critical process to enhance the mechanical properties of materials.
Let’s delve into the diverse applications of heat treatment, showcasing its vital role in shaping industries across various sectors. Join us as we navigate through eight practical examples, each illustrating how heat treatment revolutionizes manufacturing processes.

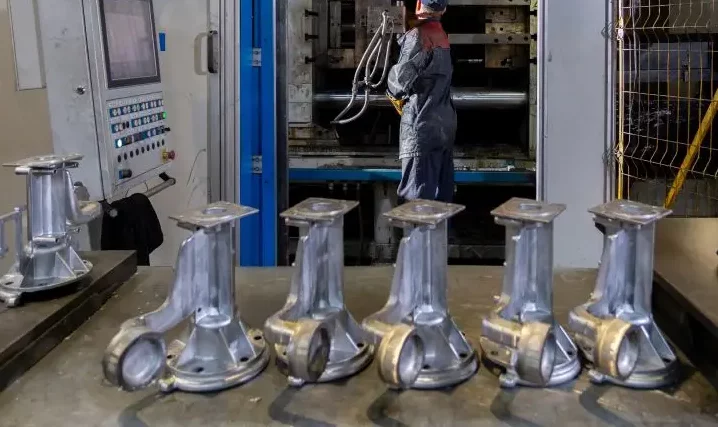
Automotive Manufacturing: Enhancing Performance and Durability
In automotive manufacturing, heat treatment is essential for enhancing the performance and durability of critical components. From engine parts to transmission gears, heat-treated materials offer increased strength, hardness, and wear resistance, ensuring optimal performance and longevity on the road.
Aerospace Engineering: Ensuring Safety and Reliability
In the aerospace industry, where safety and reliability are paramount, heat treatment plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity of aircraft components. By imparting materials with the necessary strength, fatigue resistance, and thermal stability, heat treatment ensures the safe and efficient operation of aircraft.
Tool and Die Making: Enabling Precision and Consistency
Precision is fundamental in tool and die making, where component quality directly impacts manufacturing processes. Heat treatment enables the production of tools with the required hardness, toughness, and wear resistance, ensuring precise and consistent results in metal shaping and forming applications.

Construction and Infrastructure: Enhancing Longevity and Resilience
In the construction and infrastructure sectors, heat treatment enhances the longevity and resilience of structural materials. By improving strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, heat-treated materials contribute to the durability and integrity of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects, ensuring they withstand the test of time and environmental factors.
Energy and Power Generation: Optimizing Efficiency and Reliability
In the energy and power generation industry, heat treatment is essential for optimizing the efficiency and reliability of critical components. From turbine blades to boiler tubes, heat-treated materials withstand high temperatures and harsh operating conditions, ensuring continuous and reliable energy production in power plants.
Medical Device Manufacturing: Ensuring Biocompatibility and Performance
In medical device manufacturing, heat treatment is important. It ensures that implantable materials meet stringent safety and performance standards. By subjecting materials to heat treatment, essential qualities like strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility are imparted. This guarantees the safety and effectiveness of medical implants and devices used in healthcare applications.
Defense and Military Technology: Strengthening Security and Survivability
In the defense and military sectors, heat treatment enhances the survivability of military equipment. By improving the strength, toughness, and durability of weapons and armored vehicles, heat-treated materials ensure the effectiveness and survivability of military assets in combat situations.
As industries forge ahead in innovation, the impact of heat treatment in manufacturing stands as a foundation, propelling advancements in manufacturing and engineering. With ongoing advancements and evolving techniques, heat treatment remains an indispensable tool in the ever-changing industrial landscape.


