What is lead time?
Lead time in modern manufacturing is the time elapsed from the start of a project or process until its conclusion, including delivery of a finished product. The overall production stages typically included in lead time are order processing, manufacturing, and shipping. However, the specifics of each job must always be considered. In general, a shorter lead time is preferred since it means faster product delivery. However, it should be noted that reducing the lead time of an operation may require substantial investments in automation, technology, and supply chain logistics.
How is lead time for manufacturing calculated?
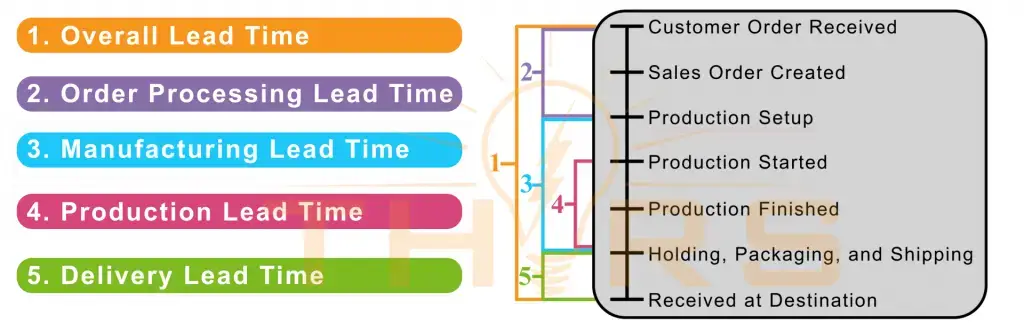
The formula for lead time in manufacturing is typically presented as lead time equals pre-processing time plus processing time plus post-processing time. Pre-processing time is the time used to prepare to manufacture parts or products. Pre-processing typically involves steps such as updating equipment, procuring raw materials, and acquiring any other components required for production. Processing time is the time used to manufacture parts or products, which varies based on the customer’s order and the operation. Post-processing time is the time used to ship finished parts or products to the customer.
What are the different types of lead time?
The implementation focus for lead time depends on the type of lead time. Some examples include:
- Order lead time, which begins when the order is received from the customer.
- Order processing lead time, or order handling lead time, which begins when the order is received and lasts until production begins.
- Manufacturing lead time, which encompasses both the pre-production time and the manufacturing process itself, or production time.
- Production lead time, which refers to the manufacturing portion of the job.
- Delivery lead time, which is the final sequence, including any holding periods, shipping, and delivery of the final product.
What are some options to improve lead time?
Lead time is an inherent part of manufacturing and product delivery; however, there are certain options to improve lead time and enhance overall efficiency.
One option to improve lead time is consolidating suppliers, which ensures that the parts required for production all arrive at the same time. Consolidating suppliers can also reduce shipping costs and simplify production scheduling. Sourcing suppliers near the manufacturer is another option to improve lead time, particularly when the supplier can monitor usage and keep the required stock on hand.
Another option to improve lead time is to outsource subassembly tasks, which can save on production lead time. If certain portions of the product assembly are too costly or difficult to manage for the manufacturer, outsourcing subassembly tasks may be an answer.
Implementing an automated inventory management system is another option to improve lead time. Inventory management systems can reduce stockouts, track inventory levels, and improve scheduling.
Understanding the basic calculation and correctly monitoring lead time are important steps for improving manufacturing efficiency. However, manufacturers must also be aware of many other parameters involved in their processes. Improvements to lead times will only be successful if team members have a strong understanding of the processing logistics involved in their operations.
THORS presents the crucial aspects of implementing lead time for manufacturing in our visual and interactive learning format. In addition, we have a diverse manufacturing excellence library covering a variety of improvement methods used in manufacturing industries. Visit thors.com to expand the knowledge and skillsets of your workforce, and to ensure that your company has the highest quality training available today.