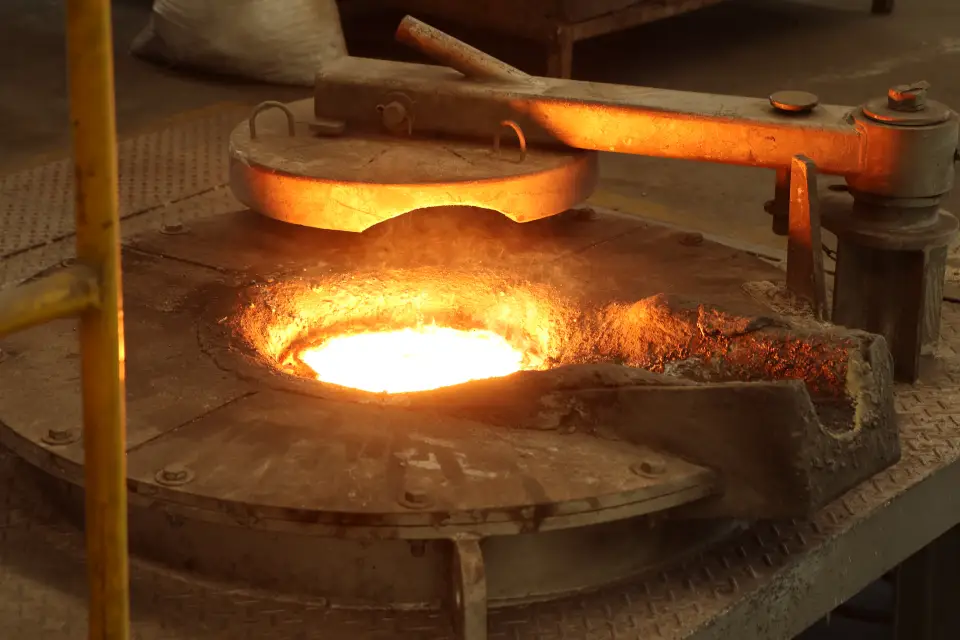
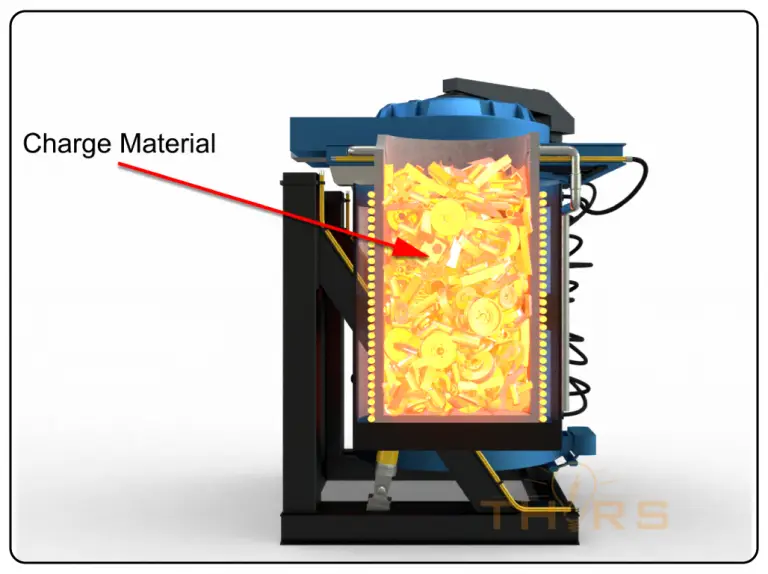
What is Induction Melting?
Induction melting occurs when an electrically conductive object, usually referred to as charge material, is placed in an alternating electromagnetic field generated within induction melting furnaces. The melted metal is then poured from the induction furnace to make castings, or cast parts, for a variety of industries, such as aviation, automotive, and agriculture. Understanding the induction melting furnace components is crucial for optimizing this process, as each component plays a specific role in ensuring the efficiency and quality of the melting operation.
What are Induction Melting Furnace Components and Systems?
Induction melting furnace components and systems are important to recognize and understand. These include the basic mechanical and structural components, the power coil system, the cooling coil system, and the flux containment system.

What are the Basic Mechanical and Structural Components of Induction Melting Furnaces?
The basic mechanical and structural components include:
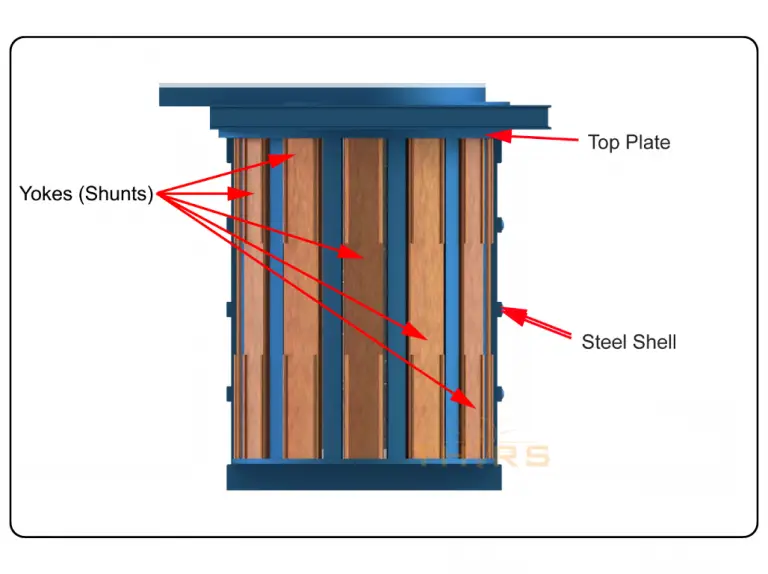
- The steel frame, or shell, functions as the main support mechanism for several other components and systems.
- The top plate keeps the coil and refractory system in compression.
- The yokes, or shunts, provide mechanical support for the coil assembly, the refractory system, and the charge material.
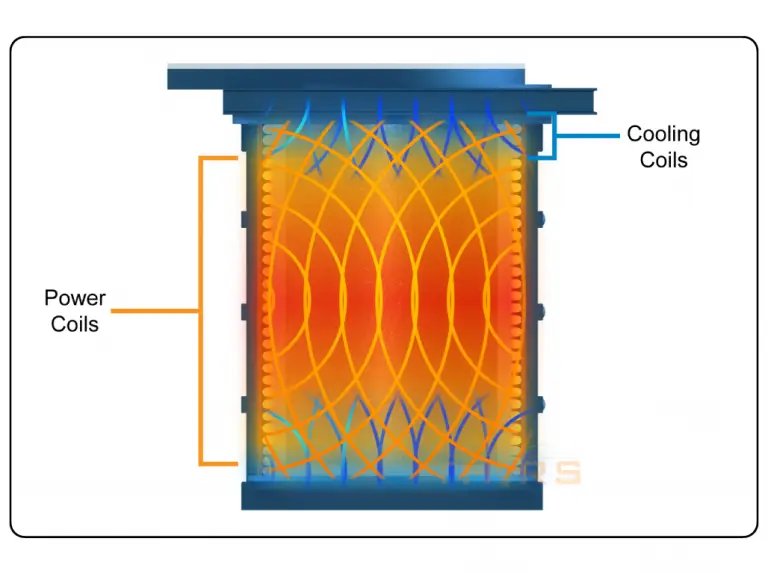
What are the Power Coil and Cooling Coils Systems for Induction Melting Furnaces?
The power coil system carries the Alternating Current, or AC, that generates the electromagnetic field required for melting. Electrically insulated to prevent arcing, the power coil consists of multiple turns of oxygen-free copper tubing which has a high electrical conductivity.
The cooling coil system works in conjunction with the power coils to provide a water-cooled plane on the backside of the furnace lining. The water-cooled plane helps to maintain the thermal gradient of the refractory system and the temperature gradient of the furnace from top to bottom. It also minimizes thermal stresses on the refractory system. Though made of stainless steel and carrying no AC current, the cooling coils do have an induced voltage and are electrically insulated.
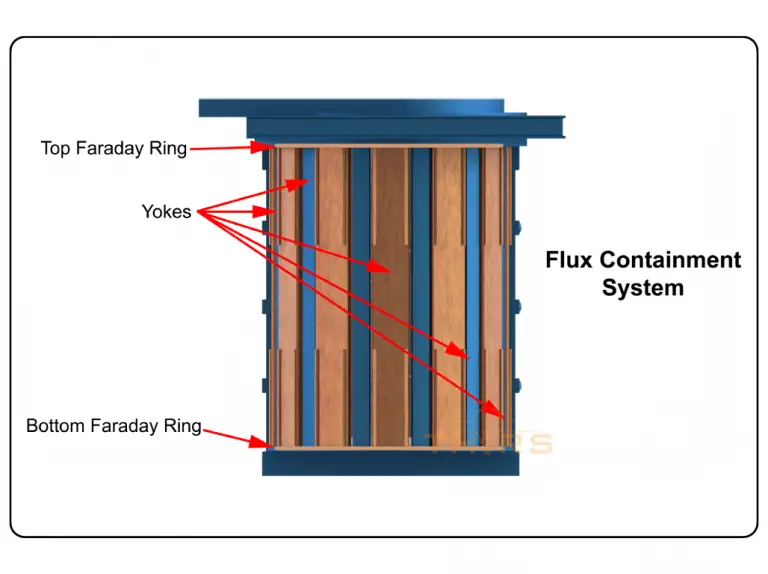
What is the Flux Containment System for Induction Melting Furnaces?
The flux containment system consists of two Frings, a top and bottom, and the yokes in between. The top Fring shields the magnetic steel lid, the top plate and the shell above from the electromagnetic field. The bottom Fring shields the magnetic steel floor and helps to direct the electromagnetic field into the bottom face of the magnetic yokes. The yokes also act as an efficient electromagnetic flux return path, preventing the field from reaching out to heat the furnace’s steel shell.
Understanding the components and systems of induction melting furnaces is crucial for practicing safe and successful induction melting. However, operators must also be aware of many other variables regarding the furnace, including the modes operation, the stirring and mixing characteristics, and the basic user controls of the system.
THORS explores the important aspects of induction melting furnaces in our visual and interactive learning format. In addition, we have a diverse castings library covering a variety of melting devices and alloys used in castings industries. Visit thors.com to expand the knowledge and skillsets of your workforce, and to ensure that your foundry has the highest quality training available today.